How Air Purifier Technology Works
In an increasingly polluted world, ensuring the air we breathe is clean and safe has become a significant concern. Air purifiers have emerged as a popular solution to combat indoor air pollution, but how do they work? In this article, we’ll delve into the technology behind air purifiers, exploring the mechanisms that allow them to improve indoor air quality.
Understanding Indoor Air Pollution
Before we delve into the working of air purifiers, it’s essential to understand indoor air pollution and its sources. Indoor environments can harbor various pollutants, including dust, pet dander, pollen, mold spores, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and even airborne viruses and bacteria. These pollutants can arise from cleaning products, cooking, smoking, and inadequate ventilation. As a result, indoor air quality can often be worse than outdoor air quality, leading to various health issues.
The Basics of Air Purifier Technology
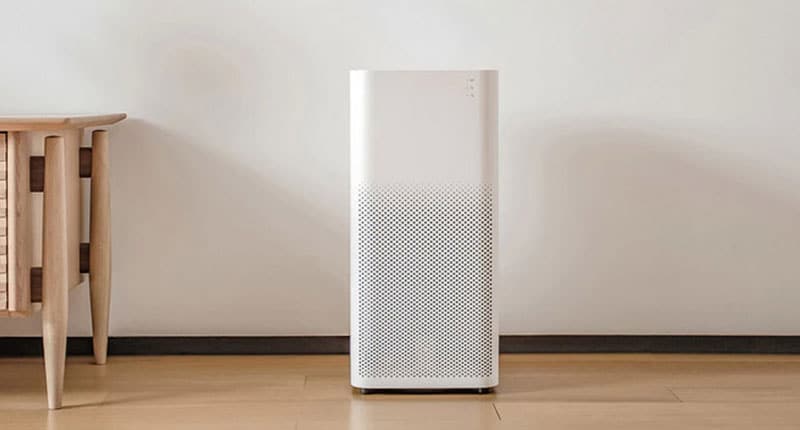
Air purifiers are devices designed to remove contaminants from the air within a confined space. They utilize various technologies to achieve this goal, and some of the most common types of air purifiers include High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filters, activated carbon filters, ozone generators, and electronic air purifiers.
HEPA Filters – Trapping Particulate Matter
One of the most widely used technologies in air purifiers is the HEPA filter. HEPA filters work by trapping airborne particles as air passes through them. These filters can capture particles as small as 0.3 microns with a high efficiency rate, making them effective against dust, pollen, pet dander, and other particulate matter. HEPA filters are especially valuable for individuals with allergies or asthma, as they can significantly reduce respiratory irritants.
Activated Carbon Filters – Absorbing Odors and VOCs
Activated carbon filters are excellent companions to HEPA filters. While HEPA filters target particulate matter, activated carbon filters specialize in adsorbing odors, gases, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). The porous structure of activated carbon allows it to trap these molecules, leaving the air smelling fresher and safer to breathe.
Experience the Future of Eyewear with Huawei x Gentle Monster
Ozone Generators – Producing Ozone for Odor Elimination
Ozone generators are controversial air purifiers due to their potential health risks when used incorrectly. These devices work by producing ozone, a gas that can react with and neutralize odors and pollutants. However, excessive ozone exposure can be harmful to the respiratory system, so ozone generators should be used cautiously and only in unoccupied spaces.
Electronic Air Purifiers – Removing Particles via Attraction
Electronic air purifiers, also known as ionizers, use an entirely different mechanism to clean the air. These purifiers release ions into the air, which attach to airborne particles, making them heavier and causing them to settle on surfaces. While this process removes particles from the air, some electronic air purifiers produce ozone as a byproduct, which may be a concern for some users.
Ultraviolet (UV) Germicidal Irradiation – Destroying Microorganisms
UV germicidal irradiation is a technology used in some advanced air purifiers to combat airborne pathogens like bacteria and viruses. These purifiers incorporate UV lamps that emit UV-C light, which damages the DNA of microorganisms, rendering them unable to reproduce and thus eliminating the risk of infection.
The Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regardless of the type of air purifier used, regular maintenance is crucial to ensure optimal performance. Filters in HEPA and activated carbon purifiers need periodic replacement, while electronic purifiers require cleaning of their plates or collection grids. Neglecting maintenance can lead to decreased efficiency and compromised air quality.
The Impact on Health and Well-being
The improvement in indoor air quality through air purifiers can have a significant impact on health and well-being. Cleaner air can reduce allergy and asthma symptoms, promote better sleep, enhance focus and productivity, and even contribute to a more positive mood.
Conclusion
Air purifiers play a vital role in ensuring clean and healthy indoor air. By understanding the different technologies behind these devices, individuals can make informed choices when selecting an air purifier that best suits their needs. Whether it’s HEPA filters for particulate matter, activated carbon filters for odors, or UV germicidal irradiation for microbial control, each technology contributes to the overall goal of cleaner and safer air.
FAQs
- Do air purifiers eliminate all types of indoor air pollutants? While air purifiers can effectively remove many common indoor air pollutants, they may not eliminate all types, such as carbon monoxide or radon. It’s essential to address the specific pollutants of concern.
- Can air purifiers help with pet allergies? Yes, air purifiers with HEPA filters can significantly reduce pet dander and other allergens, making them beneficial for individuals with pet allergies.
- How often should I replace the filters in my air purifier? Filter replacement frequency depends on the type of air purifier and usage. Generally, HEPA filters should be replaced every six months, and activated carbon filters every three months.
- Are ozone generators safe to use? Ozone generators should be used with caution as excessive ozone exposure can be harmful. It’s best to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and use them only in unoccupied spaces.
- Can air purifiers help with COVID-19 protection? While air purifiers with UV germicidal irradiation can help neutralize airborne viruses, including COVID-19, they should not be solely relied upon as the primary protective measure. Other preventive strategies, such as vaccination and mask-wearing, are also crucial.